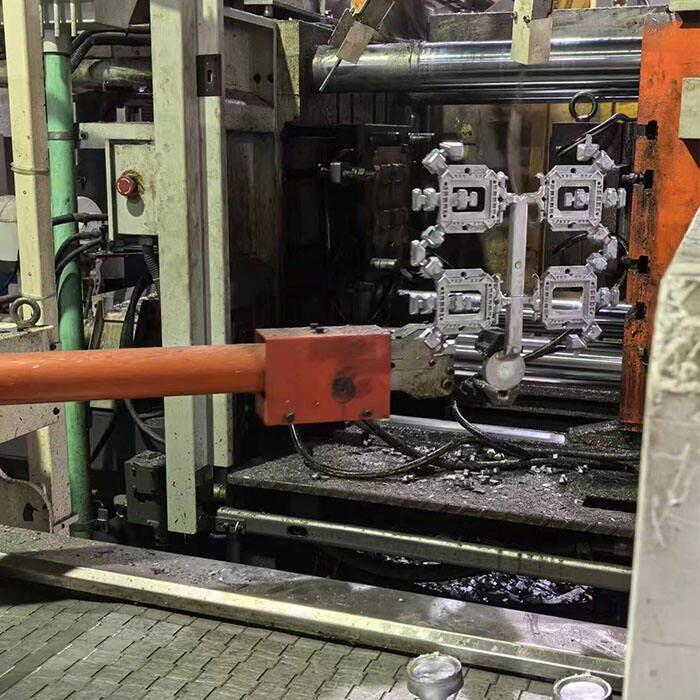
المقدمة
من بين العديد من عمليات التصنيع الموجودة، الصب الصب هو عملية مفيدة تُستخدم لإنتاج الأجزاء بكميات كبيرة. الصب بالضغط هي عملية صب معدني تستخدم المعادن المنصهرة، حيث يتم إجبارها في أشكال من خلال ضغط عالٍ حيث ستتصلب بعد ذلك وتخلق الشكل. تم تطويرها كطريقة اقتصادية لإنتاج كميات كبيرة من المنتجات، يتفوق الصب بالقالب لأن العديد من الصب يمكن أن يتم من قالب واحد مع نتائج دقيقة للغاية. ستأخذك هذه المقالة عبر الأسباب التي تجعل الصب بالقالب طريقة تصنيع شائعة جدًا عبر الصناعات.
II. مزايا الصب باستخدام القوالب
A. كفاءة الإنتاج العالية
للحصول على دورة إنتاج سريعة، يمكن إنتاج القطع خلال بضع ثوانٍ. بالنظر إلى أن صب القوالب هو أحد أسرع العمليات لإنتاج القطع، فإن هذه الميزة من حيث السرعة، بالإضافة إلى الإنتاج العالي والعمليات الآلية التي تتم بسرعة تعمل على تقليل التوقف عن العمل - وهو ما يحدث غالبًا عندما يتجاوز الطلب العرض.
ب. الدقة وتحمل الأبعاد
بما أنهم يتم معالجتهم باستخدام قوالب الصب، واحدة من السمات هي الدقة في الصب بالمolds. استخدام هذه التقنية يضمن إنتاج القطع بدقة وكفاءة عالية وإعادة إنتاج مطلوبة لتطبيقات تتطلب تناسب ودقة الوظيفة. الدقة في قطع الصب تحتاج إلى تشغيل ما بعد الصب بشكل ضئيل، مما يبسط الإنتاج.
ج. مرونة التصميم
الدقة في صب القوالب تعطيه ميزة على معظم الأشكال الأخرى من الإنتاج القابل للتنفيذ، مما يسمح بتصميمات أكثر تعقيدًا مما يمكن إنتاجه في العمليات البديلة من المعدن المنصهر. تم تصميم هذه التقنية لمعالجة الجدران الرقيقة، التفاصيل الدقيقة والتعقيدات الداخلية للأجزاء التي تواجه طرق التصنيع التقليدية صعوبة في تقليدها، مما يجعل العملية أكثر ملاءمة لمجموعة أوسع من التطبيقات.
ثالثًا. ملاءمة المواد
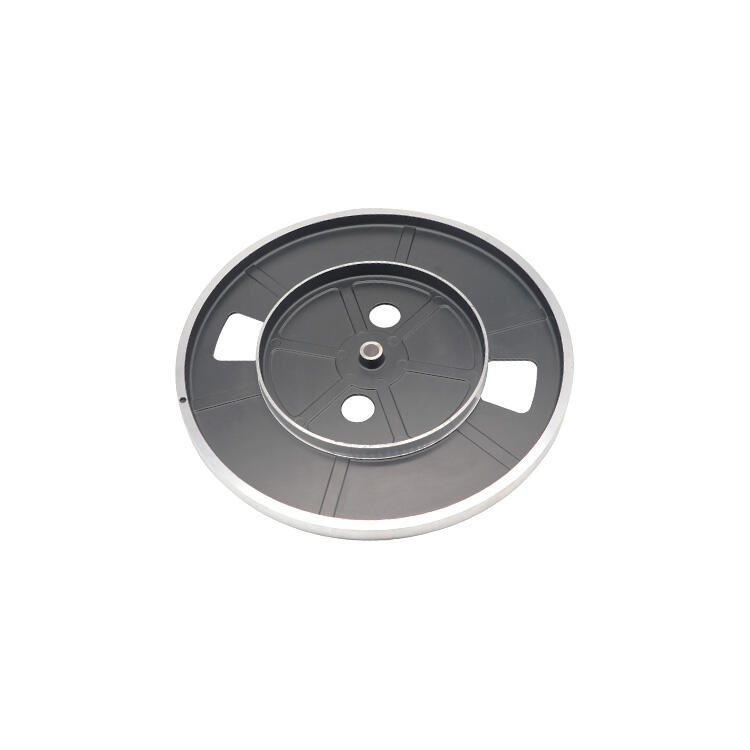

أ. مواد صب القوالب الشائعة
صب القوالب متعدد الاستخدامات ويمكنه التعامل مع نطاق واسع من المواد. تعتبر سبائك الألمنيوم، الزنك، المغنيسيوم والنحاس من بين أكثر المواد شيوعًا المستخدمة لأن كل منها يمتلك خصائص فريدة تتناسب مع التطبيقات النهائية المحددة التي يمكنها تقديمها.
ب. بعض خصائص المواد التي جعلت صب القوالب مشهورًا
يتم تصنيع السيارة من أنواع مختلفة من المواد التي يمكن استخدامها في صب القوالب، ولكن اختيار المادة في عملية الصب لا يعتمد فقط على ما يمكن صبه، بل يعتمد أيضًا على الجودة التي تقدمها المادة للمنتج النهائي. قطع الصب الألمنيوم خفيفة الوزن ولديها قابلية جيدة لنقل الحرارة، مما يجعلها خيارًا جيدًا لقطع السيارات أو مبردات الحرارة في الإلكترونيات، كمثالين محتملين للاستخدام.
IV. الفعالية التكلفة
أ. تكلفة الأدوات المنخفضة
صب القوالب — الطبيعة القابلة لإعادة الاستخدام للقوالب تعني أن عملية صب القوالب غالبًا ما تتمتع بتكلفة أدوات أقل عند مقارنتها بالطرق الأخرى. تكلفة القالب هي الاستثمار الأولي، لكن تكلفة القطعة الواحدة يمكن أن تنخفض بشكل كبير عند إنتاج كميات كبيرة.
ب. تقليل هدر المواد
بما أن صب القوالب دقيق للغاية، فإنه يستخدم كمية أقل من المواد، مما يجعل العملية الإنتاجية بأكملها فعالة. ليس هذا فقط يقلل من التكاليف، ولكنه يتماشى أيضًا مع نوع العمليات التصنيعية الصديقة للبيئة التي تصبح شائعة بشكل متزايد.
ج. اقتصاديات حجم الإنتاج الضخم
بما أن قوالب الصب بالضغط يمكنها إنشاء أجزاء بكميات كبيرة في الساعة، فهي طريقة تصنيع اقتصادية تتجاوز نطاق الطرق التقليدية التي تؤدي إلى امتصاص التكاليف العمالية والمادة بشكل غير متناسب.
خ. تطبيقات الصناعة
أ. صناعة السيارات
قطاع السيارات هو المستخدم النهائي الأكثر شيوعًا، حيث يتم استخدام الصب بالضغط لإنتاج أجزاء المحركات والمركبات الهيكلية. حقيقة أن العناصر المصبوبة خفيفة الوزن وقوية هي العامل الحاسم في توفير الوقود وتحسين الأداء.
ب. صناعة الطيران والفضاء
يُستخدم الصب بالضغط في صناعة الطيران لصنع أجزاء خفيفة الوزن تعمل تحت ظروف شديدة للغاية. دقتها وقوتها تجعلها مثالية للاستخدام في الطائرات وكذلك مكونات المركبات الفضائية.
ج. الإلكترونيات الاستهلاكية
الإلكترونيات الاستهلاكية، على سبيل المثال، تحتاج دائمًا إلى أجزاء دقيقة يمكن إنتاجها بكميات كبيرة جدًا: صب القوالب مثالي. تُستخدم عمليات صب القوالب بشكل أساسي لصب أغطية الأجهزة والأجزاء الدقيقة الصغيرة.
VI. الاعتبارات البيئية
أ. فعالية الطاقة في عملية صب القوالب
هذه العملية أكثر كفاءة من حيث استهلاك الطاقة مقارنة بعمليات الصب الأخرى مثل صب الرمل أو التشكيل بالاستثمار، ويمكن أن تساعد في تقليل بصمة الكربون للتصنيع.
ب. إعادة استخدام المواد والاستدامة
بسبب هذا * معظم مواد صب القوالب قابلة لإعادة التدوير وتساعد على اقتصاد دائري يعود بالنفع أيضًا لأن معظم المادة يمكن إعادة تدويرها مرة أخرى في صناعة ذات مساهمة إنسانية رائدة.
ج. تقييم دورة حياة منتجات صب القوالب
بالتأكيد، مراجعة نقدية لنتائج تقييم دورة الحياة لمنتجات صب القوالب تسهل تسليط الضوء على ملفها البيئي الإيجابي عبر جميع مراحل الإنتاج حتى مرحلة إعادة التدوير عند نهاية العمر الافتراضي.
VII. الجودة والدقة
أ. مقارنة مع عمليات التصنيع الأخرى
ليس فقط أن صب القوالب يعطي هذه المجموعة من الخصائص، ولكنه أيضًا أسرع بكثير من عمليات مثل التشكيل أو التجهيز. قد تكون القطع المُشكلة أكثر قوة من صب القوالب، لكن الأمثلة أعلاه تثبت أن المرونة في التصميم والاقتصاد في التكلفة يمكن أن تكون لصالح طريقة صب القوالب. العمليات الميكانيكية لديها دقة عالية، لكنها أكثر تكلفة وأبطأ.
ب. السيطرة على جودة صب القوالب
صب القوالب يتمتع بشكل طبيعي بالقابلية للتكرار، ويسمح العملية بتطبيق بروتوكولات فحص صارمة للحفاظ على جودة عالية للقطع، مما يمكّن من التحكم الأفضل على جودة صب القوالب.
ثامناً. القيود والحلول
أ. قيود المواد
إنه متعدد الاستخدامات، لكنه ليس المثالي لجميع المواد. اسمح لي أن أشرح. ومع ذلك، فإن التقدم في علوم المواد يستمر في توسيع مجموعة المواد التي يمكن اعتبارها مرشحة لصب القوالب.
ب. قيود التصميم
يمكن التغلب على قيود صب القوالب المتعلقة بزوايا المسح وحركات النواة من خلال تصميم إبداعي أو باستخدام المساعدة التقنية. مبادئ الهندسة. ج .
ج. التغلب على التحديات من خلال تحسين العمليات
لقد تحسنت تقنية صب القوالب بشكل كبير عبر السنوات، مما جعلها تقنية فعالة وعملية مُحسّنة تجعل النتائج موثوقة من خلال التغلب على التحديات مثل المسامية، وعدم الاستقرار البعدي وغيرها.
IX. الاتجاهات المستقبلية والابتكارات
أ. الطفرة التكنولوجية في صب القوالب
بالنسبة لصب القوالب، هذا يعني عادةً برامج المحاكاة في التصميم والتحقيق في التلقائيّة على مستوى المصنع وحتى على مستوى المعالجة.
ب. اعتماد مواد جديدة
عملية صب القوالب تشهد تطوير وإدخال مواد جديدة مثل السبائك عالية القوة، والمركبات لتوفير مجالات تطبيق أوسع من قبل.
ج. التكامل مع تقنيات التصنيع الأخرى
صب القوالب يصبح أكثر اندماجًا مع تقنيات التصنيع الأخرى، على سبيل المثال طباعة ثلاثية الأبعاد للأدوات أو استخدام تقنية التراص بالليزر المباشر (DMLS) للنوى المعقدة لتمكين فرص ابتكارية جديدة.
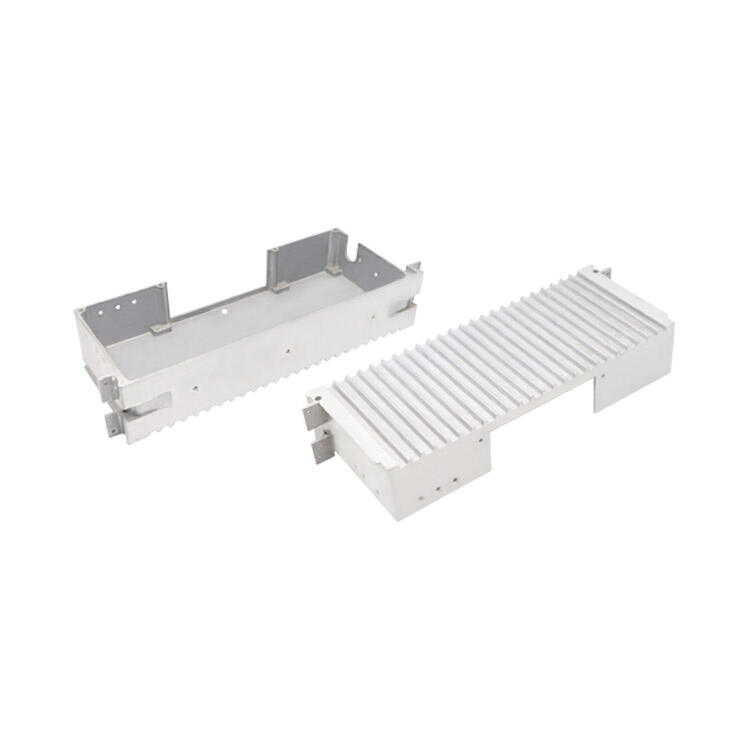

X. الاستنتاج
يشير شعبيتها في التصنيع إلى مرونتها لصناعة القرن الحادي والعشرين. الكفاءة، الدقة، المواد، نقطة السعر قابلية التكيف إلى أي تطبيقات تجعله هائلا في صناعة التصنيع. مع تحسين التكنولوجيا بشكل متزايد وسد الفجوة بين تقنيات الصب المطبوعة التقليدية ، ستستمر تقنيات الأدوات السريعة في اكتساب قوة تأثير كجزء أساسي من رؤية أوسع للتصنيع.

